Difference between revisions of "PGP382"
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
'''Application:''' | '''Application:''' | ||
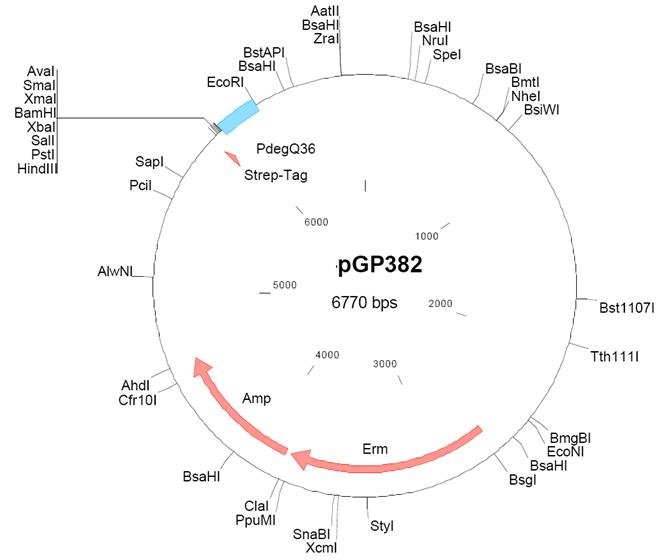
| − | The vector was constructed in the [[Stülke]] lab and it is suitable for constitutive overexpression of C-terminally Strep-tagged proteins in ''B. subtilis''. The plasmid confers resistance to ampicillin and erythromycin in ''E. coli'' and ''B. subtilis'', respectively. | + | The vector was constructed in the [[Stülke]] lab and it is suitable for constitutive overexpression of C-terminally Strep-tagged proteins in ''B. subtilis''. The plasmid confers resistance to ampicillin and erythromycin in ''E. coli'' and ''B. subtilis'', respectively. pGP382 can be used for the [[SPINE]] method. [[pGP380]] is similar to the vector pGP382 which is derived from vectors [[pBQ200]] and [[pHT315]]. A Shine-Dalgarno sequence has to be fused to the open reading frame during PCR. |
Sequencing primers: | Sequencing primers: | ||
Revision as of 11:58, 25 February 2010
Application:
The vector was constructed in the Stülke lab and it is suitable for constitutive overexpression of C-terminally Strep-tagged proteins in B. subtilis. The plasmid confers resistance to ampicillin and erythromycin in E. coli and B. subtilis, respectively. pGP382 can be used for the SPINE method. pGP380 is similar to the vector pGP382 which is derived from vectors pBQ200 and pHT315. A Shine-Dalgarno sequence has to be fused to the open reading frame during PCR.
Sequencing primers:
- M13_puc_for: 5‘-GTAAAACGACGGCCAGTG-3‘
- M13_puc_rev: 5‘-GGAAACAGCTATGACCATG-3‘
Christina Herzberg, Lope Andrés Flórez Weidinger, Bastian Dörrbecker, Sebastian Hübner, Jörg Stülke, Fabian M Commichau
SPINE: a method for the rapid detection and analysis of protein-protein interactions in vivo.
Proteomics: 2007, 7(22);4032-5
[PubMed:17994626]
[WorldCat.org]
[DOI]
(P p)